



You will be using the program SYBYL for this assignment. SYBYL is a powerful molecular modeling and visualization program for SGI and Linux workstations. It has many functions, but today you will be using only the most basic of them.
Open another Unix Shell (go to Desktop -> Open Unix Shell, give your PERM number again) and then type:
sybyl
Remember that Unix is case sensitive and you have to use spaces between commands and file names. Resize the windows so that both this tutorial and the SYBYL program are visible. The SYBYL program has two windows: the dark-slate-gray visualization area, and the black text area. The program reports results of its operations in the black text area. For example, when you read in the DNA structure file, the nucleotide sequence will be echoed to the text area; when you measure distances, the results of the measurements will be shown in the text area. I recommend that you leave the bottom of the screen for the SYBYL text window, place this tutorial on the left side of the screen, and work on the right side with SYBYL. To resize a window, simply drag one of its edges.
You will now analyze the structure of a short double-helical DNA molecule. DNA is the molecule that carries our hereditary information. DNA can occur in a couple of different forms but the one you will be working with is the most common form, also known as the B-DNA. To open the structure file containing the coordinates of DNA follow the steps below:
In the 'File' menu, select 'Open'
Select file DNA.pdb in the ../MOL directory, and hit OK to open the file.
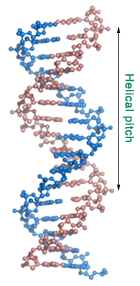
Before you proceed, take a moment and look at the DNA molecule in front of you. You are looking down the helical axis and are seeing a somewhat symmetrical placement of components that make up the DNA double helix.
| Action | Direction | Mouse button |
|---|---|---|
| Move | Left/Right/Up/Down | Middle |
| Rotate | At any angle | Right |
| Rotate | In plane | Left+Right |
| Zoom | In/Out | Middle+Right |
Rotate the molecule into the upright position and zoom out until the whole molecule fits into the screen. Can you recognize a double helix? Can you identify the major and minor grooves?
Zoom in so that you can clearly see one nucleotide. Can you recognize the three components — the nucleobase, the deoxyribose sugar ring, and the phosphodiester bond — that make up a nucleotide?
Assignments (DNA): |
|
|---|---|
|
 |
 Remember, this is an idealized view of a double-stranded DNA. Real DNA in the cell is not as regular, it is surrounded by water and counterions, and interacts with proteins. The figure on the right illustrates how the protein called 'catabolite gene activator protein', or CAP interacts with double-stranded DNA and bends it. Interaction with different proteins helps to pack large DNA molecules into the cell nucleus or allows the regulation of gene expression.
Remember, this is an idealized view of a double-stranded DNA. Real DNA in the cell is not as regular, it is surrounded by water and counterions, and interacts with proteins. The figure on the right illustrates how the protein called 'catabolite gene activator protein', or CAP interacts with double-stranded DNA and bends it. Interaction with different proteins helps to pack large DNA molecules into the cell nucleus or allows the regulation of gene expression.
You can further explore the structure of DNA via animated tutorials by Eric Martz at http://www.umass.edu/molvis/tutorials/dna/. The CAP protein and DNA bending are further described in a Chime-based tutorial from Massey University. Please note that you need a Chime plug-in to see this structure. The plug-in is not installed on Linux.

